Title: Analyzing the Ecosystem of Blockchain Data
In the realm of technology and finance, blockchain has emerged as a transformative force, offering decentralized solutions across various industries. One of its pivotal components is the data ecosystem within blockchain networks. This article delves into the intricacies of blockchain data ecosystems, analyzing their structure, significance, and future prospects.
Understanding Blockchain Data Ecosystems
At its core, a blockchain is a distributed ledger that records transactions across a network of computers in a secure and transparent manner. Each block in the chain contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, creating a secure link between them. This structure ensures the immutability and integrity of the data stored on the blockchain.
The data ecosystem within a blockchain comprises various elements:
1.
Transaction Data:
This includes information about transactions conducted on the blockchain, such as the sender, receiver, amount, timestamp, and transaction ID. Transaction data is crucial for auditing, tracing, and validating transactions on the network.2.
Smart Contracts:
Smart contracts are selfexecuting contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. They automate and enforce the execution of agreements on the blockchain, eliminating the need for intermediaries and enhancing efficiency.3.
Consensus Mechanisms:
Consensus mechanisms, such as Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS), govern how transactions are validated and added to the blockchain. These mechanisms ensure agreement among network participants and maintain the integrity of the data ecosystem.4.
Decentralized Applications (DApps):
DApps are applications built on top of blockchain platforms, utilizing smart contracts to enable decentralized functionality. They interact with the underlying blockchain's data and logic, fostering innovation and new use cases.5.
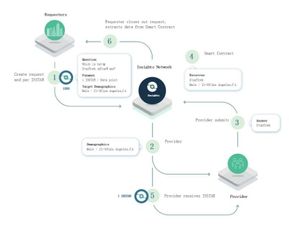
Onchain and Offchain Data:
Onchain data refers to information stored directly on the blockchain, while offchain data resides outside the blockchain but is linked to it through various means, such as oracles or offchain protocols. The interplay between onchain and offchain data expands the scope and utility of blockchain applications.Significance of Blockchain Data Ecosystems
The data ecosystem within blockchain networks holds immense significance for several reasons:
1.
Transparency and Immutability:
By design, blockchain technology ensures transparency and immutability of data, fostering trust among network participants. Once recorded, data on the blockchain cannot be altered or deleted without consensus, enhancing the integrity of transactions.2.
Security and Trust:
The decentralized nature of blockchain networks, coupled with cryptographic techniques, enhances security and mitigates the risk of fraud or unauthorized access. Participants can trust the integrity of the data and the validity of transactions without relying on intermediaries.3.
Efficiency and Automation:
Smart contracts automate the execution of agreements, streamlining processes and reducing the need for manual intervention. This improves efficiency, reduces costs, and minimizes the potential for human error.4.
Interoperability and Scalability:
Blockchain data ecosystems are evolving to facilitate interoperability between different blockchains and traditional systems. This interoperability, along with advancements in scalability solutions, expands the potential applications of blockchain technology across industries.5.
Data Monetization and Innovation:
The data generated and stored within blockchain ecosystems can be leveraged for various purposes, including analytics, insights, and monetization. This datadriven approach fosters innovation and creates new opportunities for businesses and developers.Future Prospects and Challenges
Looking ahead, the future of blockchain data ecosystems presents both opportunities and challenges:
1.
Scalability:
Scalability remains a key challenge for blockchain networks, especially as they aim to support a growing number of transactions and users. Innovations such as sharding, layer 2 solutions, and consensus algorithm enhancements are being explored to address scalability concerns.2.
Regulatory Landscape:
The regulatory environment surrounding blockchain and cryptocurrency continues to evolve, impacting the development and adoption of blockchain data ecosystems. Clear and consistent regulations are essential to foster innovation while ensuring consumer protection and financial stability.3.
Interoperability Standards:
Establishing interoperability standards between different blockchain networks and traditional systems is crucial for seamless data exchange and collaboration. Industry initiatives and standards bodies are working towards interoperability frameworks to enable frictionless interaction between diverse platforms.4.
Privacy and Security:
Protecting the privacy of sensitive data while maintaining the security of blockchain networks is a complex challenge. Innovations in zeroknowledge proofs, homomorphic encryption, and privacyfocused protocols aim to address privacy concerns without compromising security.5.
Sustainability:
The energy consumption associated with certain consensus mechanisms, such as Proof of Work, raises concerns about the environmental impact of blockchain networks. Transitioning to more energyefficient consensus mechanisms and exploring sustainable blockchain solutions are imperative for longterm viability.In conclusion, the ecosystem of blockchain data is a fundamental aspect of blockchain technology, driving transparency, security, efficiency, and innovation across various industries. By understanding its structure, significance, and evolving landscape, stakeholders can harness the full potential of blockchain data ecosystems while addressing existing challenges and shaping the future of decentralized technologies.